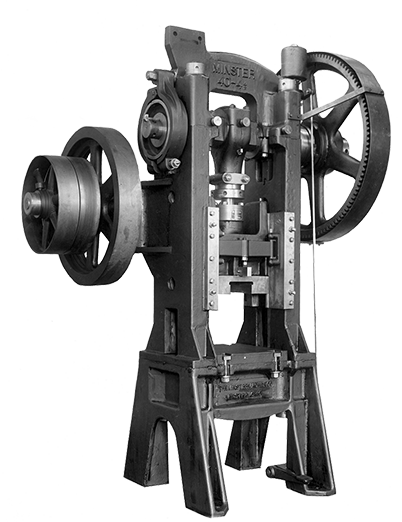
First use of straight side single crank press design, patented in 1934.
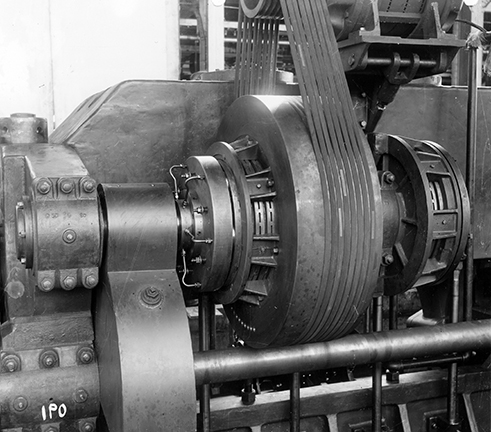
First use of a separate multiple disc air friction clutch and separate multiple disc air friction brake on the same shaft.
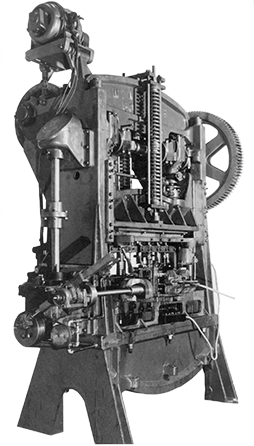
World’s first transfer-type mechanical press built.
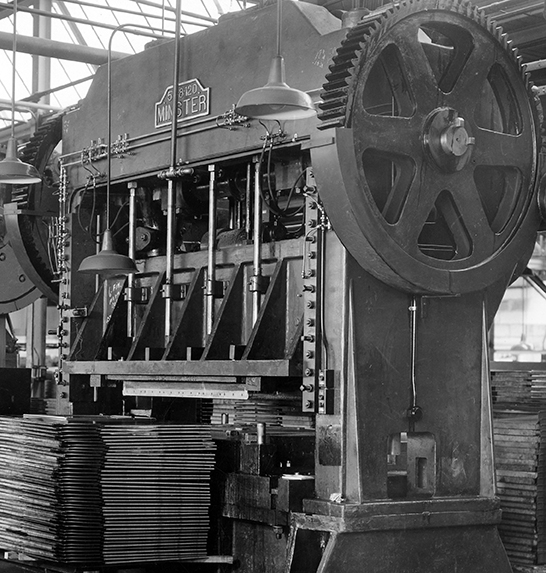
First press company to offer full box-type crown and press construction.
Began use of patented Air Operated Friction Clutch and Brake Unit (AFC).
First press company to offer box construction in large “C” frames and slides.
Began incorporating barrel-type slide adjustment in press designs.
First to offer recirculating oil lubrication on presses.
First use of patented Combination Air Friction Clutch and Brake (CFC) mounted on crankshaft in either flywheel or main gear and having controlled torque.
Began use of patented Minster rotor-type rotary limit switch.
First press company to offer replaceable bronze-lined wear surfaces throughout a press.
First P2 Piece-Maker press built for automatic progressive die applications.
First use of clutch-in-gear application.
First MS2 press built with clutch on intermediate shaft near the intermediate gear.
First to offer motorized inclining of very large gap frame presses.
First G1 Series presses are built.
First E2 press built. First presses in the industry to work with large progressive dies, providing greater geared press speeds.
First press company to offer special crown with front and back cabinets to enclose electrical and air systems.
First tear-top can end press built.
First can draw press built.
First press company to offer a quick die change system — The Die-Namic Process.
First F2 (Fin-Maker) press built for stamping of heat transfer fins.
MonitorFlow lubrication system is patented.
The Stamping Center is first displayed — the world’s first totally automated stamping production system.
The first Hummingbird press is built capable of speeds up to 1,600 strokes-per-minute — more than four times faster than the fastest press at that time.
Developed and patented a line of ultra high speed cam feeds along with material handling system which included a reel, straightener, and patented “S” loop.
Developed and patented rotary balancers to retrofit with P2 presses, which increased maximum running speed.
Development of PM2 lamination press began. This included hydrostatic gibs for which patents were granted.
First Piece-Maker II (PM2) built with reciprocating balancers.
First programmable Logic Controller used in press controls.
First line of rack and pinion feeds were developed and patented.
First servo-driven electronic high speed feed.
First electronic servo feed.
First TR2 (Pulsar) built.
First use of Minster/Orii robotic handling system for OBI presses.
First piston-driven cupper press developed with flexdisc hydraulic clutch and auxiliary belt-driven flywheel.
First material handling reel built.
First die cart built.
First color (CRT) operation interface fully automated press control.
Developed and patented ECH-125 end conversion press which included piston drive, quick lift slide, micro-adjustable bolster and disc brake.
Developed and built a granulator system for rubber tire recycling.
First Minster/Tranemo hydraulic presses with robotic Flexarm built.
Developed and patented a dynamic balanced double action shell and cupper press.
First P2H press built with patented adjustable stroke mechanism.
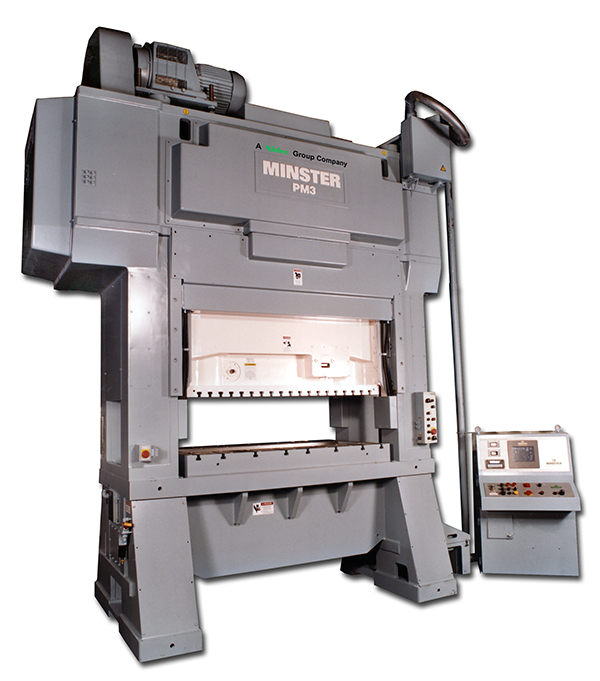

Developed PM3 press series with patented adjustable-in-motion (AIM) slide.
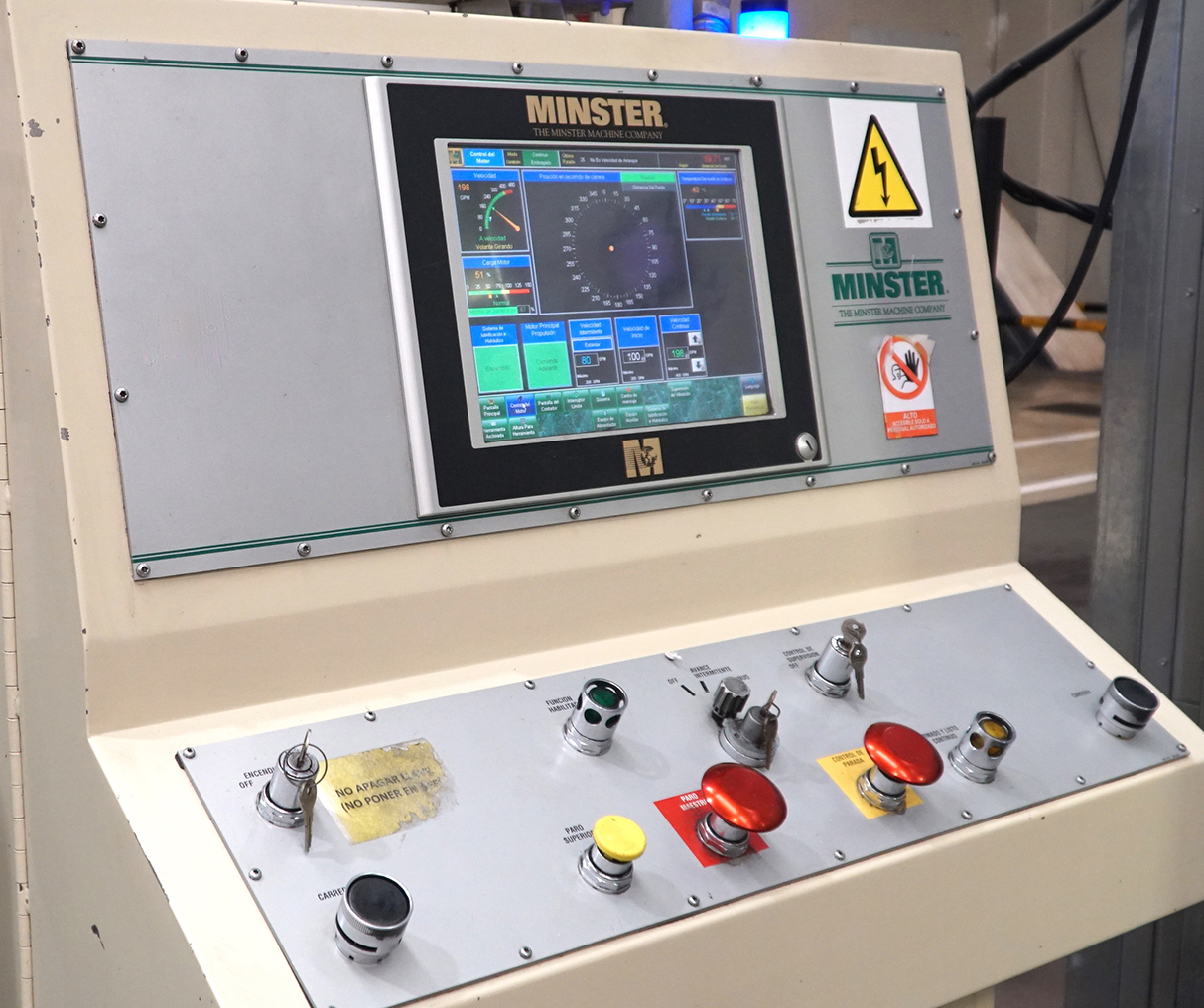

Introduction of Production Management Control, fully integrating press, tool and coil line functions.
Developed CRH underdrive opposed ram press for production of beverage cans made from laminated film material.
First Allen-Bradley PMC (Production Management Control) with gray scale screen.
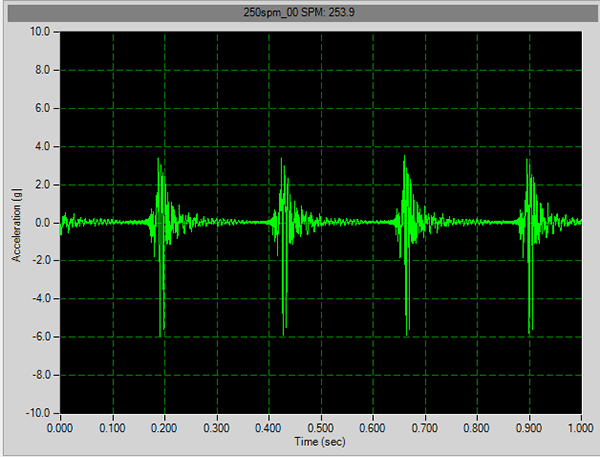
Developed and pateneted vibration severity, load monitoring and die process technology.
Developed first vari-slide infinitely adjustable slide motion mechanism.

First TwinTec forming/assembly machine developed in cooperation with the Otto Bihler Company.
Developed PMConnect software for production monitoring and system reporting.
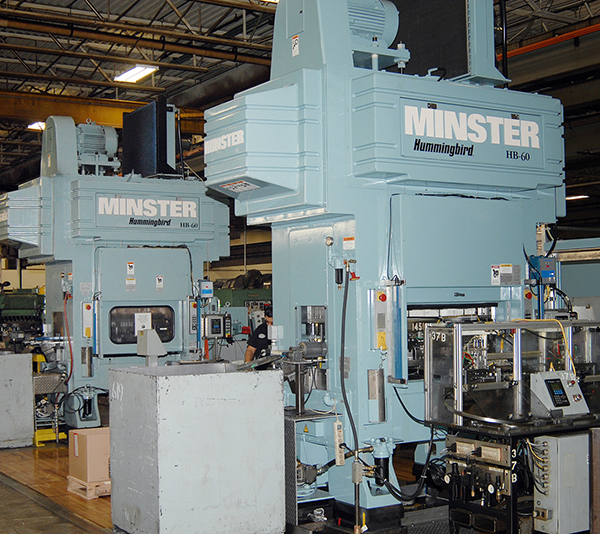

Intoduction of “new” Hummingbird Series of press, designed for high speed motor lamination production.
First press manufacturer in the world to offer infinitely adjustable stroke feature.
Began remote access to controls in the field.

Developed PM4-600 press — largest motor lamination press at the time.
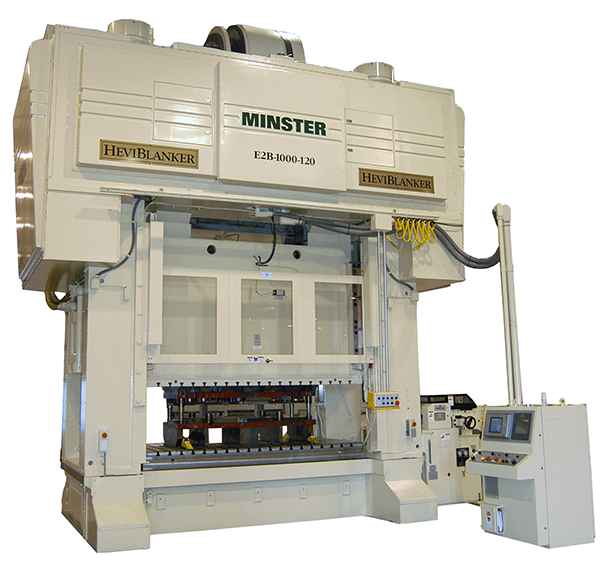
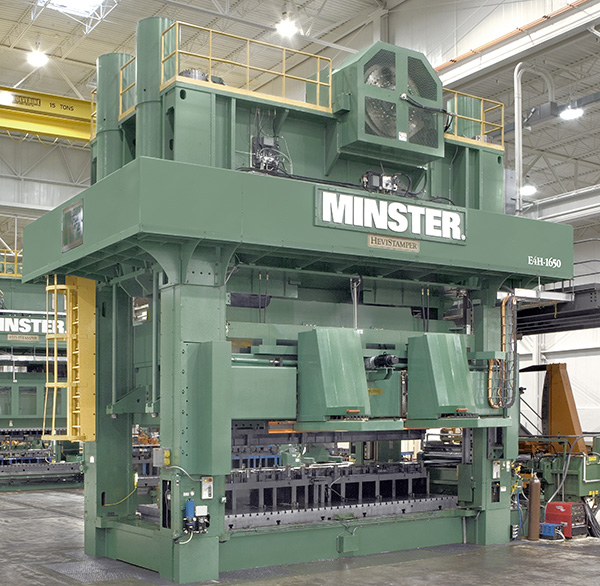


Developed E2B-1000 (HeviBlanker) press for high speed blanking of extremely high strength material.
Developed eccentric link driven E4H large tonnage/big bed press line. World’s first four-point press with quick lift feature.

Developed HB-60 (Hummingbird) model.

Developed E2H-1100.
Developed World’s first “Dual Energy Drive System” for mechanical presses.
Developed EFAC clutch brake, first zero backlash air clutch designed for high reverse torque loads, utilizing two sets of flex discs.

Developed high speed servo lamination notching press and system.

First PMC-based servo press control.

The DAC-H165 cupper press launches, significantly improving productivity for customers in the container industry.

FieldHawk becomes a standard press control feature.
First use of Mitsubishi PMC and Siemens PMC.

The ECH-140 press launches, significantly improving productivity. This press is the first to offer Adjust in Motion (AIM) capabilities in the container market.
Servo press control is branded GPC (Global Production Control).
Developed APMACS Beckhoff IPC-based control









